Graphic The relentless rise of carbon dioxide Ancient air bubbles trapped in ice enable us to step back in time and see what Earth's atmosphere, and climate, were like in the distant past They tell us that levels of carbon dioxide (CO 2) in the atmosphere are higher than they have been at any time in the past 400,000 years This indicator describes how the levels of major greenhouse gases in the atmosphere have changed over time Figure 1 Global Atmospheric Concentrations of Carbon Dioxide Over Time This figure shows concentrations of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere from hundreds of thousands of years ago through 19, measured in parts per million (ppm) The graphs show monthly mean carbon dioxide measured at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii The carbon dioxide data on Mauna Loa constitute the longest record of direct measurements of CO 2 in the atmosphere They were started by C David Keeling of the Scripps Institution of Oceanography in March of 1958 at a facility of the National Oceanic and

Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
Greenhouse gas graph
Greenhouse gas graph-At the global level, the gases shown in the pie chart (at right) represent the key greenhouse gases emitted by human activities These gases are most closely documented in studies of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions Image (at right) Carbon greenhouse gas emissions by gas Source IPCC (07);A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and ozone (O 3)Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth's surface would



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
This chart shows the change in global greenhouse gas emissions over time Greenhouse gases are measured in 'carbon dioxideequivalents' (CO 2 e) Today, we collectively emit around 50 billion tonnes of CO 2 e each year This is more than 40% higher than emissions in 1990, which were around 35 billion tonnesThis graph shows the heating imbalance in watts per square meter relative to the year 1750 caused by all major humanproduced greenhouse gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons 11 and 12, and a group of 15 other minor contributorsRio Brazos Distillery, College Station, Texas 15K likes Rio Brazos Distillery is Brazos County's first and only distillery creating slow artisan whiskey in the heart of Aggieland
Climate change includes both global warming driven by humaninduced emissions of greenhouse gases and the resulting largescale shifts in weather patterns Though there have been previous periods of climatic change, since the midth century humans have had an unprecedented impact on Earth's climate system and caused change on a global scale The largest driver of warming is The first graph shows monthly means for the last four years plus the current year, and the second graph shows the full NOAA timeseries starting in 19 Values for the last year are preliminary, pending recalibrations of standard gases and other quality control steps Other impacts on the latest few months of data are described belowBased on global emissions from 04
This graph shows the heating imbalance in watts per square meter relative to the year 1750 caused by all major humanproduced greenhouse gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons 11 and 12, and a group of 15 other minor contributorsExplore this interactive graph Click and drag to display different parts of the graph To squeeze or stretch the graph in either direction, hold your Shift key down, then click and drag The graph shows the average of a set of temperature simulations for the th century (black line), followed by projected temperatures for the 21st century based on a range of emissions scenarios (coloredGlobal warming is the unusually rapid increase in Earth's average surface temperature over the past century primarily due to the greenhouse gases released as people burn fossil fuels The global average surface temperature rose 06 to 09 degrees Celsius (11 to 16° F) between 1906 and 05, and the rate of temperature increase has nearly




This Graph Shows How The Total Amount Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Has Been Increasing Around The World Greenhouse Gases Climate Change Greenhouse Gas Emissions




This Graph Shows The Increase In Greenhouse Gas Ghg Concentrations In Download Scientific Diagram
The new facility will pipe the greenhouse gas to an oil field for use underground in enhanced oil recovery (NRG Energy photo) NRG Energy Texas has set another record The Lone Star state emits The greenhouse gas emissions graph for different means of transportation consists of seven line time series graphs with their metric tons of greenhouse gasesThe California greenhouse gas (GHG) Inventory compiles statewide anthropogenic GHG emissions The graphs below provide a summary of emissions data for 18 or for the time series of 0018 All GHG inventory data is available on the current inventory page
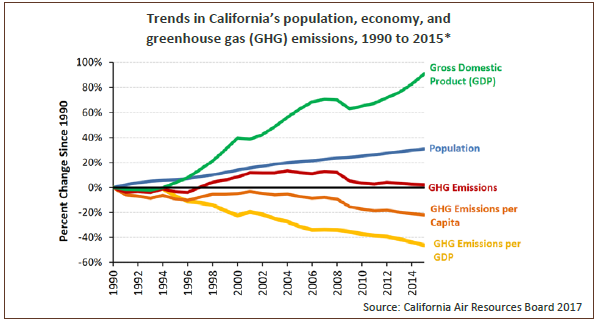



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Oehha
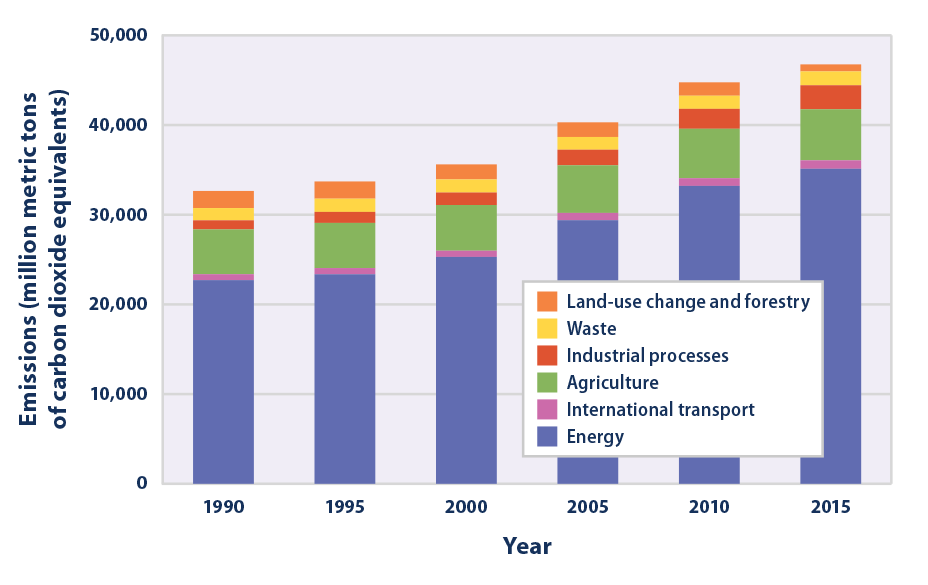



W Edyfjigr0fxm
In the Nov 14, 19 "What's Going on in This Graph," we saw that nearly a third of the United States carbon dioxide emissions (greenhouse gases), which cause global warming, is Deforestation and Greenhouse Gases Report Human activities produce large amounts of greenhouse gases (GHGs), primarily carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), and thus contribute to global warming The use of fossil fuels is the primary source of CO 2 emissions, but the removal of trees from forested land has also contributedThe planet's average surface temperature has risen about 212 degrees Fahrenheit (118 degrees Celsius) since the late 19th century, a change driven largely by increased carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere and other human activities 4 Most of the warming occurred in the past 40 years, with the seven most recent years being the warmest The years 16 and are tied for




The Role Of Animal Agriculture On Greenhouse Gas Emissions




Noaa S Greenhouse Gas Index Up 41 Percent Since 1990 Welcome To Noaa Research
To prevent severe climate change we need to rapidly reduce global greenhouse gas emissions The world emits around 50 billion tonnes of greenhouse gases each year measured in carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 eq) 1 To figure out how we can most effectively reduce emissions and what emissions can and can't be eliminated with current technologies, we need to Drop in sensitive greenhouse gases Methane, CH 4, is a another important greenhouse gas and a sensitive indicator of climate changes and temperature fluctuations Methane is formed byData Trends in CO 2, CH 4, N 2 O, SF 6 Obs ervation Pack age Marine Boundary Layer Reference Data Archive Products CarbonTracker CO 2 CarbonTracker CH 4 CarbonTracker Lagrange Power of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Index Information Figures Education How CO 2 is Measured Isotope Measurements WMO Standard Gas Comparisons
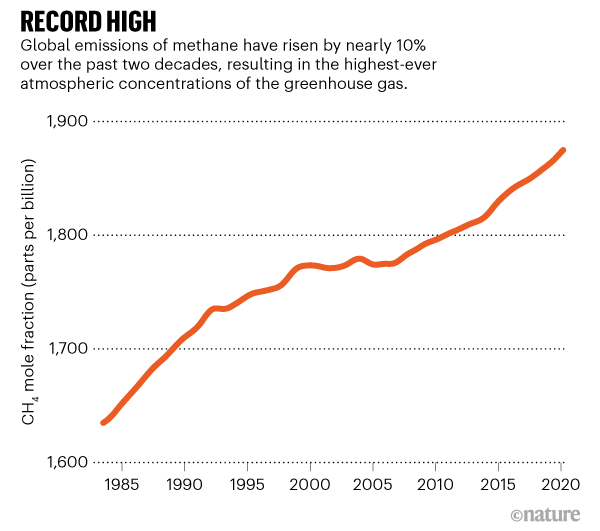



Global Methane Levels Soar To Record High




Despite Pandemic Shutdowns Carbon Dioxide And Methane Surged In Welcome To Noaa Research
Graphic A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect Perhaps the most impressive of cloud formations, cumulonimbus (from the Latin for "pile" and "rain cloud") clouds form due to vigorous convection (rising and overturning) of warm, moist and unstable air Based on data from the WRI's CAIT Climate Data Explorer, the graphic shows emissions data from 12 by country As a whole, the world emitted 42,386 megatonnes of greenhouse gases Here's howGreenhouse Gas Emissions Project Created wellbore diagrams, depth curves, and other reports and graphs as needed Languages German Groups Oil and Gas Professionals




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Plunged 17 Percent During Pandemic The Washington Post



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
To prevent severe climate change we need to rapidly reduce global greenhouse gas emissions The world emits around 50 billion tonnes of greenhouse gases each year measured in carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 eq) 1 To figure out how we can most effectively reduce emissions and what emissions can and can't be eliminated with current technologies, we need to first Greenhouse gas emissions in 14 were 9 percent below 05 levels The graphs below provide an overview of greenhouse gas emissions in the United States based on information from the Inventory Click the links below each chart to learn more about each of these topics Methane Ozone Nitrous oxide Chlorofluorocarbons Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmth The big trick of a greenhouse is that it doesn't let that warmth escape




This Graph Shows The Increasing Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases In Download Scientific Diagram




Changes Since The Industrial Revolution American Chemical Society
Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is an important heattrapping (greenhouse) gas, which is released through human activities such as deforestation and burning fossil fuels, as well as natural processes such as respiration and volcanic eruptions The first graph shows atmospheric CO 2 levels measured at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii, in recent years, with average seasonal cycleHuman emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases – are a primary driver of climate change – and present one of the world's most pressing challenges 1 This link between global temperatures and greenhouse gas concentrations – especially CO 2 – has been true throughout Earth's history 2 To set the scene, let's look at how the planet has warmedMain Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs lived




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
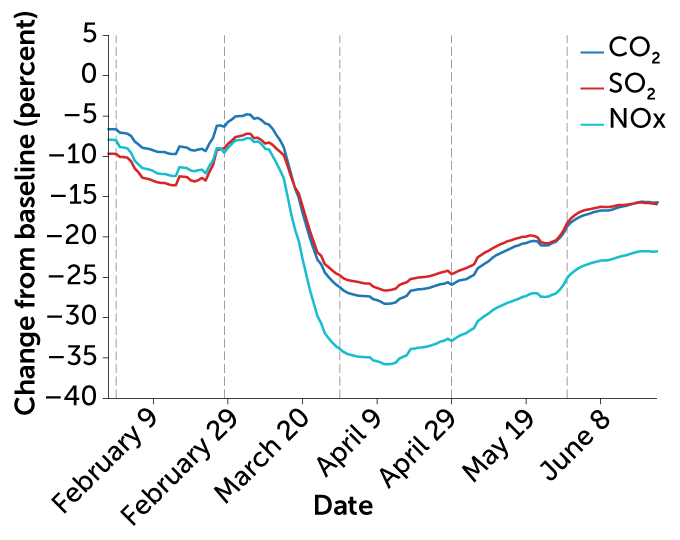



Covid 19 S Emissions Reductions Won T Impact Climate Change Science News
Greenhouse gases come from all sorts of everyday activities, such as using electricity, heating our homes, and driving around town The graph to the right shows which activities produce the most greenhouse gases in the United States These greenhouse gases don't just stay in one place after they're added to the atmosphereThis graph displays the breakdown of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by economic sector GHG emissions from the transportation sector increased 233% from 1990 to 18 This growth contrasts with the electricity sector, which was the highestemitting sector until transportation surpassed itSulfur hexafluoride (SF 6) is an extremely potent greenhouse gas SF 6 is very persistent, with an atmospheric lifetime of more than a thousand years Thus, a relatively small amount of SF 6 can have a significant longterm impact on global climate change SF 6 is humanmade, and the primary user of SF 6 is the electric power industry Because of its inertness and dielectric properties, it is
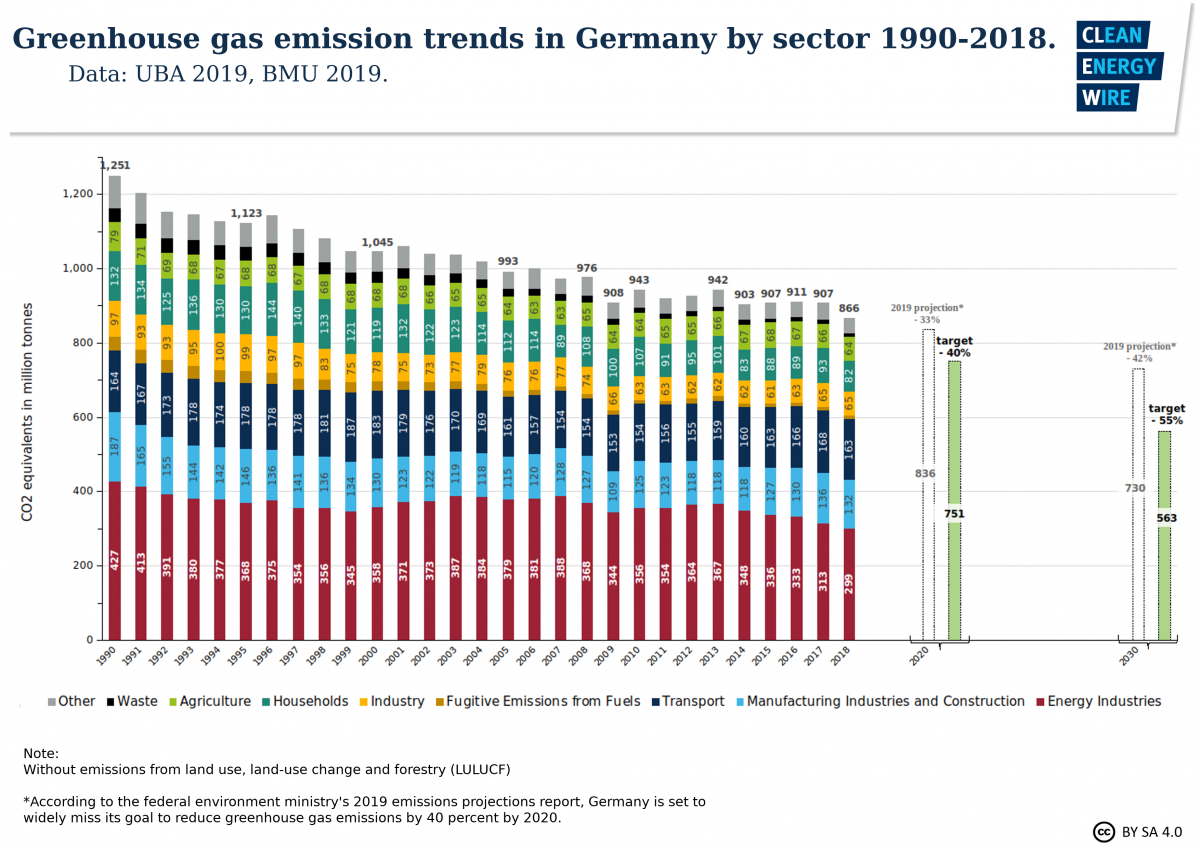



Germany Sees Largest Emissions Drop Since 09 Recession Clean Energy Wire



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
Data for the past 00 years show that the atmospheric concentrations of CO 2, CH 4, and N 2 O – three important longlived greenhouse gases – have increased substantially since about 1750 Rates of increase in levels of these gases are dramatic CO 2, for instance, never increased more than 30 ppm during any previous 1,000year period in this record but has already risen by 30 This graph shows the increase in greenhouse gas (GHG) concentrations in the atmosphere over the last 2,000 years Increases in concentrations of these gases since 1750 are due to human activities in the industrial era Concentration units are parts per million (ppm) or parts per billion (ppb), indicating the number of molecules of the Daily chart Greenhousegas emissions are set to rise fast in 21 Last year's decline, caused by the pandemic, will probably be shortlived Apr th 21 A YEAR AGO, as countries locked down




Nau Study Indicates That U S Cities Underestimate Their Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Nearly Percent On Average Research
.png)



Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Waste Products Eurostat News Eurostat
Carbon dioxide and methane are greenhouse gases and the similarity between the graphs for their concentrations and the temperature change graph indicates that the greenhouse effect is real and that it has been around for many thousands of years Carbon dioxide is a common gas present in the atmosphere It has an important role in the greenhouse effect, with other gases like methane The greenhouse effect allows the life on Earth, catchingYou can view graphs showing how the amount of carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, and various chlorofluorocarbons have changed over time at any NOAA sampling site Additional data such as isotopic ratios of carbon and oxygen species and solar radiation are
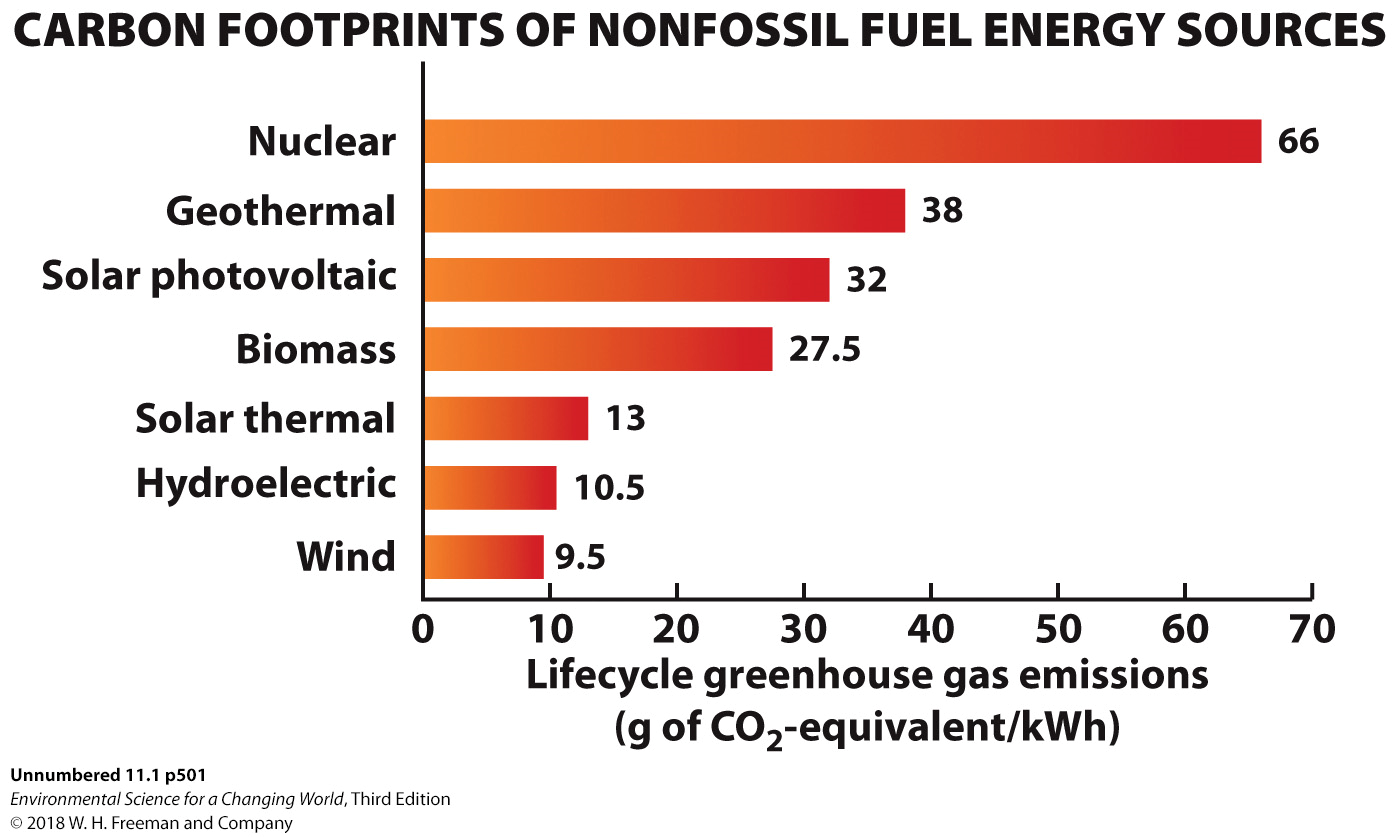



The Graph Illustrates The Lifecycle Greenhouse Gas Chegg Com
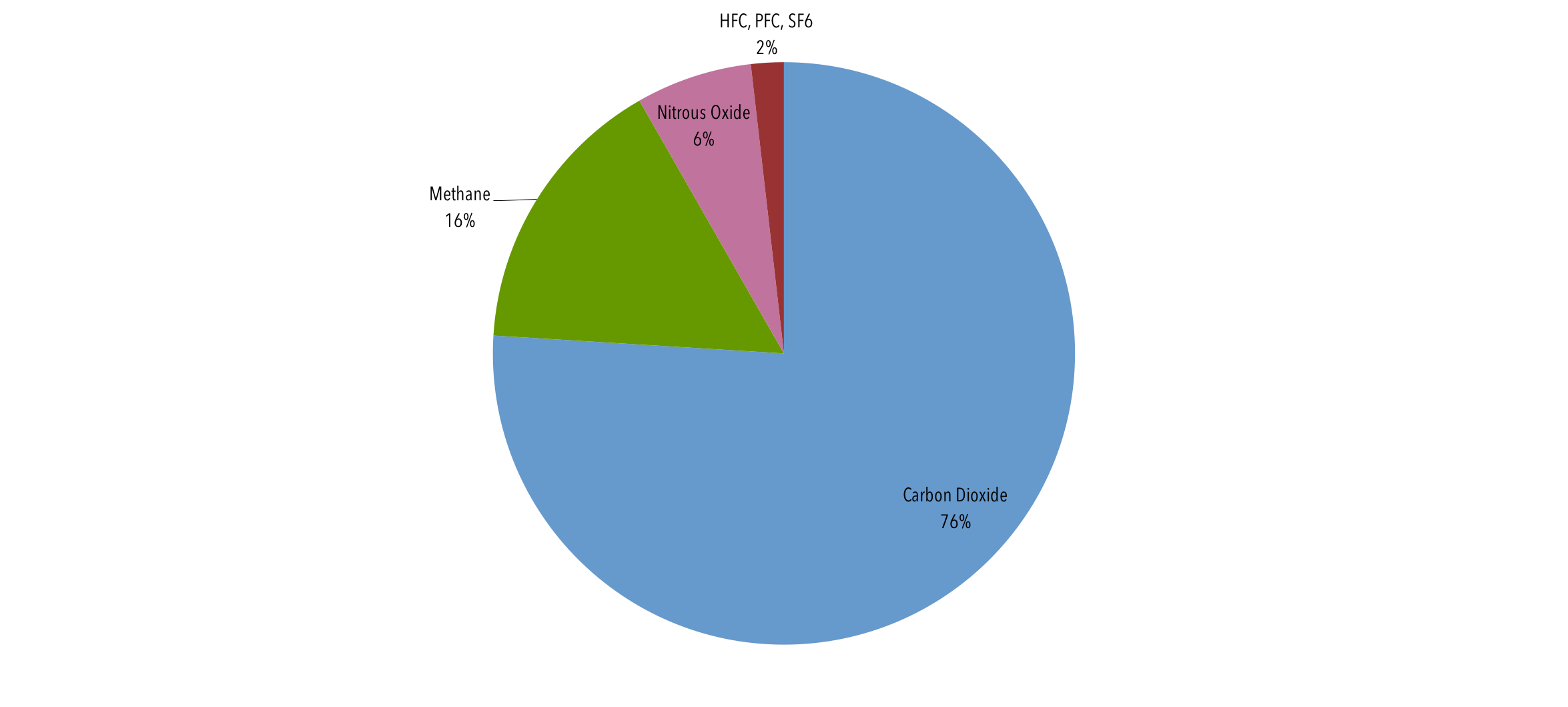



Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions
Greenhouse gas emissions are greenhouse gases vented to the Earth's atmosphere because of humans the greenhouse effect of their 50 billion tons a year causes climate changeMost is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels coal, oil and natural gasThe largest polluters include coal in China and large oil and gas companies, many stateowned by OPEC and Russia0018 GHG Inventory ( Edition) The California Greenhouse Gas Emissions for 00 to 18, Trends of Emissions and Other Indicators, summarizes and highlights the major annual changes and notable longerterm trends of each year's GHG inventory It provides easytoread graphs and explanations to illuminate California's progress in its commitment to reduce climateThe greenhouse effect of the gases is the same on the clear and the cloudy night but it is much colder without the clouds It is not obvious how to combine measures of the prevalence of greenhouse gases with the prevalence of clouds to come up with a single measure of the absorption potential of the atmosphere The graph below gives the




The Graph Gives Information On Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions From Industries Which Questions Would Brainly Com




What Are The Greenhouse Gas Emissions Of A Mini Grid Project And How Are They Calculated Mini Grids Support Toolkit Energy U S Agency For International Development
New Zealand's greenhouse gas emissions is a direct measure of the 'Human activities generating greenhouse gases' topic Stats NZ and the Ministry for the Environment must report on topics related to the five environmental domains air, atmosphere and climate, fresh water, land, and marine Vital Signs of the Planet Global Climate Change and Global Warming Current news and data streams about global warming and climate change from NASA The pie chart below shows total US emissions from the US Greenhouse Gas Inventory for 18 by sector Total US emissions in 18 were 6,677 Million Metric Tons CO 2 e The pie pieces colored in blue and purple represent the sectors that contain facilities reporting direct emissions to the Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program
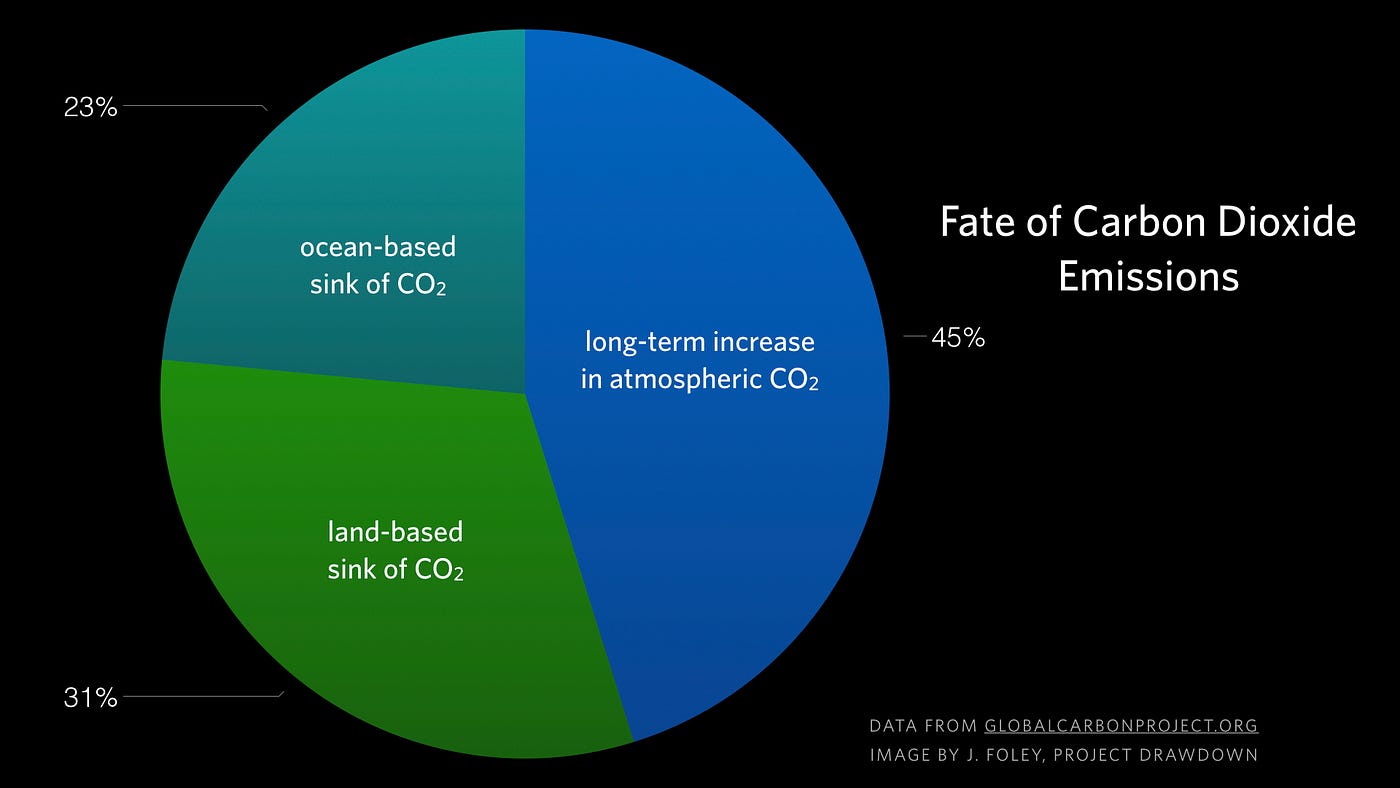



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
Other gases (CFC12, HCFC22, Perfluoromethane CF4, and Sulfur Hexaflouride SF6) 2% Produced by industrial processes As you can see, energy related CO 2 and CH 4 accounts for 90 percent of the total greenhouse gas emissions in the United States This highlights the impact of energy use on the environmentCarbon dioxide (CO 2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activitiesIn 19, CO 2 accounted for about 80 percent of all US greenhouse gas emissions from human activities Carbon dioxide is naturally present in the atmosphere as part of the Earth's carbon cycle (the natural circulation of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and animals)



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau



1



Graph Of The Day Antropocene Atmospheric Experiment Ghg Climate Forcing Increased 29 Over Years Bits Of Science




Carbon Dioxide Levels Continue At Record Levels Despite Covid 19 Lockdown World Meteorological Organization
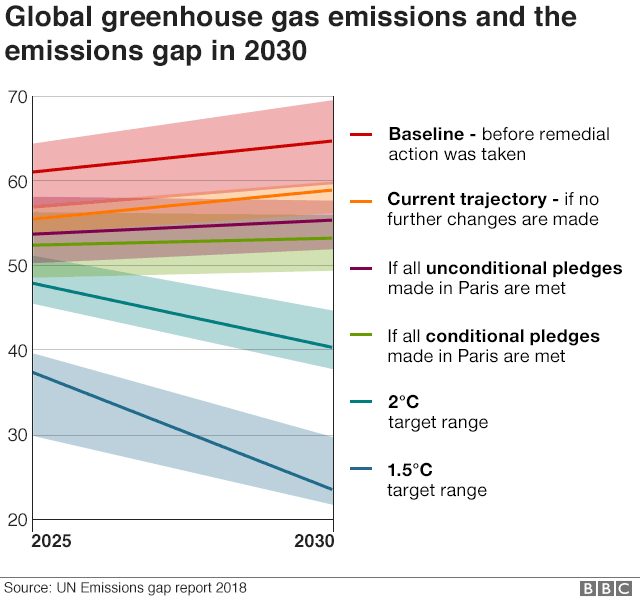



Climate Change Co2 Emissions Rising For First Time In Four Years c News



10 Uconn Greenhouse Gas Inventory Office Of Sustainability




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science




Colorado Major New Greenhouse Gas Report Explained Westword
.png)



Fact Sheet The Growth In Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Commercial Aviation White Papers Eesi



Ghg Reduction Sustainability And Public Health Mndot
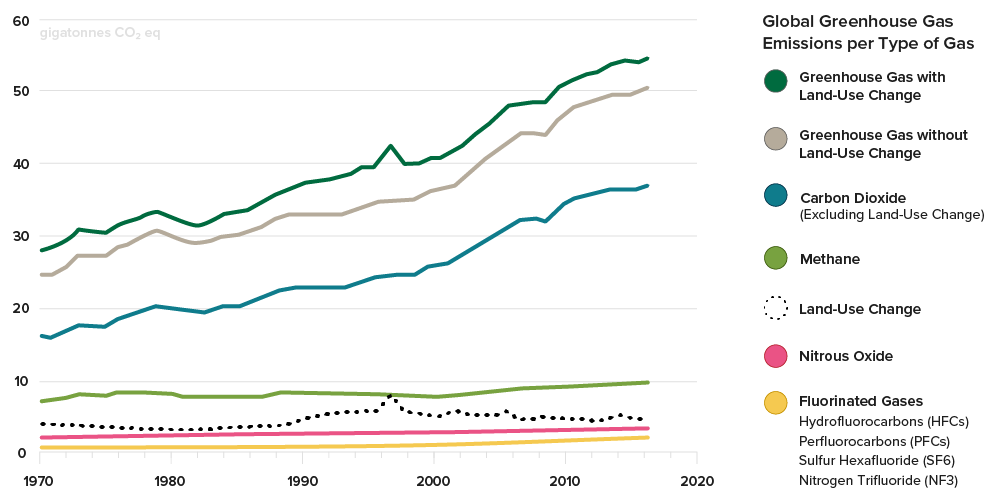



Carbon Emissions Forestry Carbon Credits The Arbor Day Foundation




Line Graph Of Global Carbon Emissions From Fossil Fuels It Shows A Slow Increase From About 500 Million M Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Emissions Emissions
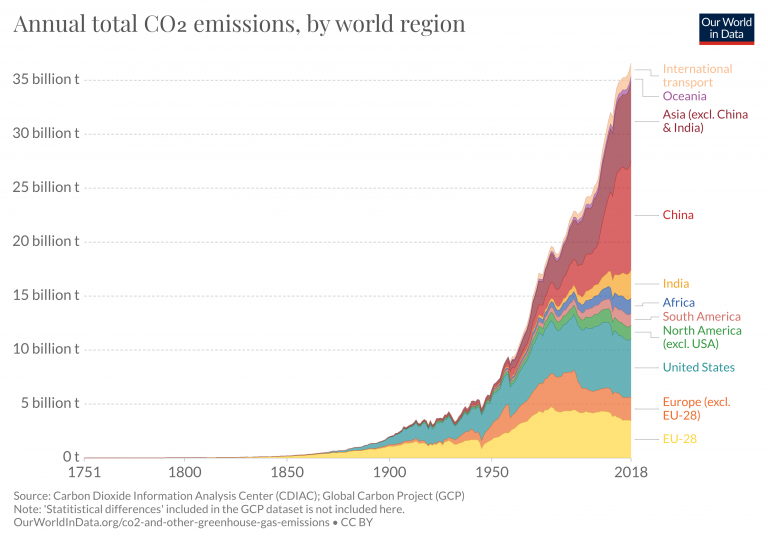



Co2 Emissions Our World In Data




Line Graph Of Global Carbon Dioxide Emissions From Fossil Fuels It Shows A Slow Increase From About 500 Mi Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gases Emissions



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Usgcrp Indicator Details Globalchange Gov




Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Manufacturing Industry Umweltbundesamt




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions
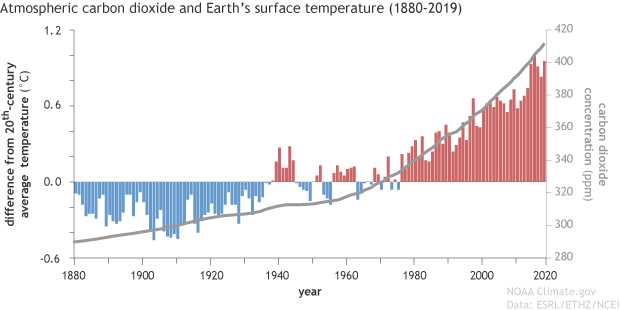



If Carbon Dioxide Hits A New High Every Year Why Isn T Every Year Hotter Than The Last Noaa Climate Gov




Climate Change Indicators U S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa




A Graph Of Per Capita Income Versus The Per Capita Greenhouse Gas Download Scientific Diagram




What S Going On In This Graph Nov 19 The New York Times




If You Re For Pipelines What Are You Against Darrin Qualman
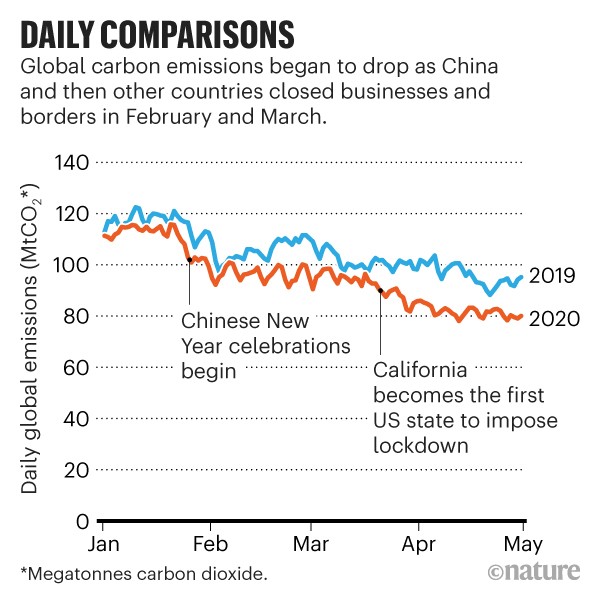



How The Coronavirus Pandemic Slashed Carbon Emissions In Five Graphs




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Plunged 17 Percent During Pandemic The Washington Post



Carbon Footprint Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Surge To New Record World Meteorological Organization
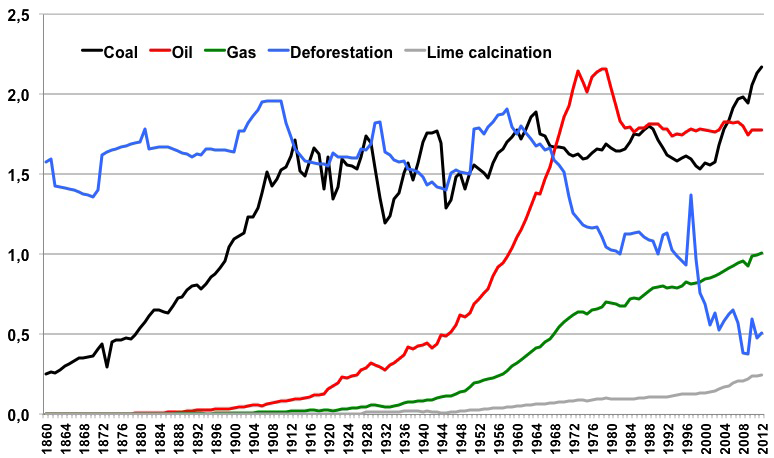



How Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Presently Evolve Jean Marc Jancovici



Q Tbn And9gcrevtfvebbghz5zkkbq1akjhfs4 Gwdrbwpqnmfiixo2oqlgyw8 Usqp Cau
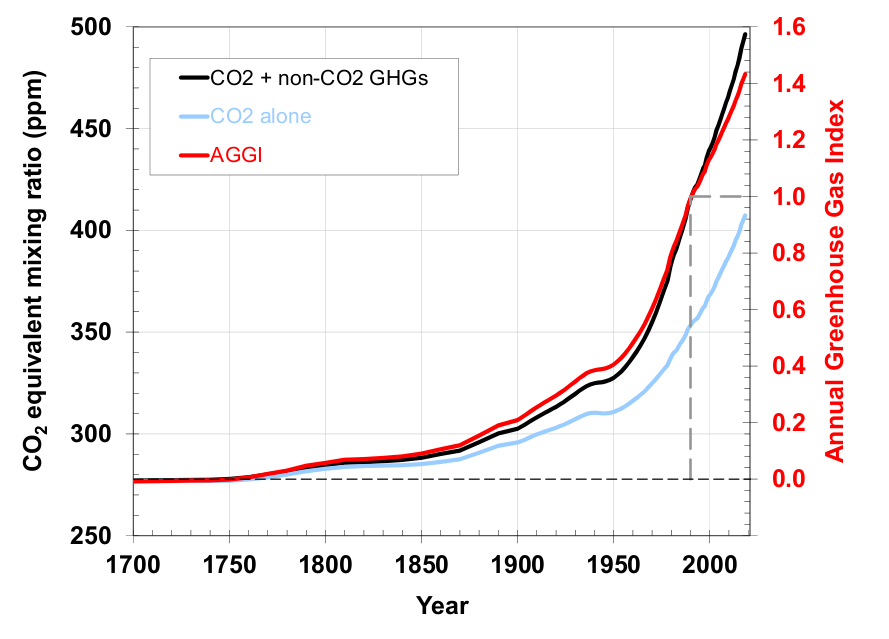



Graph Of The Day Noaa Annual Greenhouse Gas Index 1700 18 Desdemona Despair
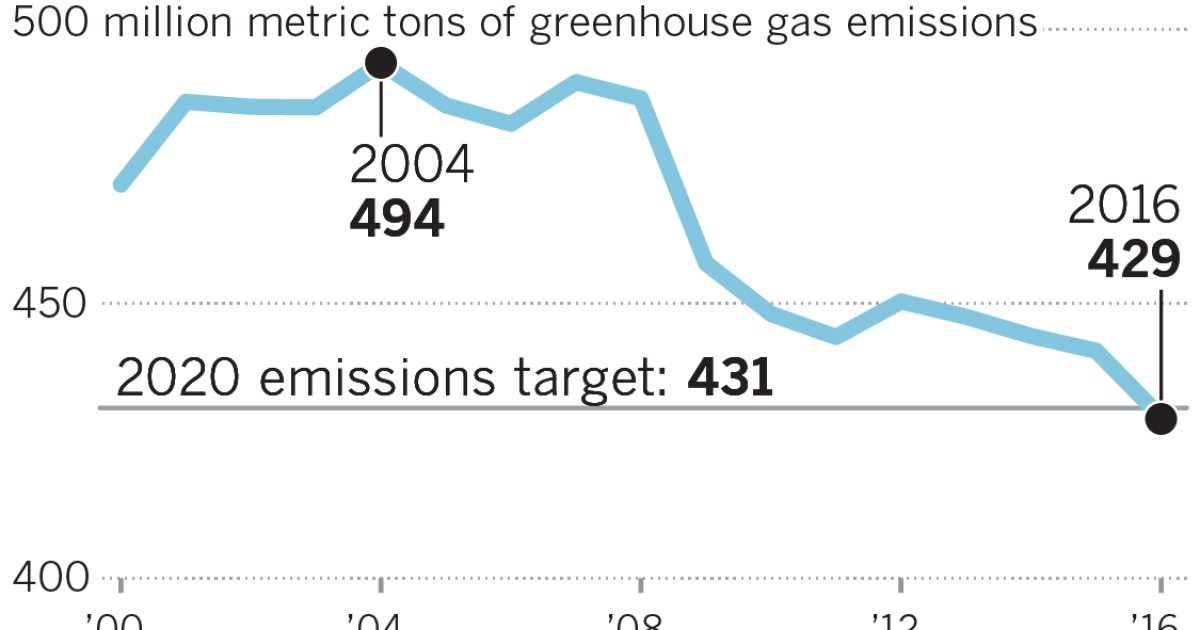



California Hit Its Climate Goal Early But Its Biggest Source Of Pollution Keeps Rising Los Angeles Times




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Agriculture Sector Emissions Climate Change Greenhouse Gas Emissions Emissions Applied Economics
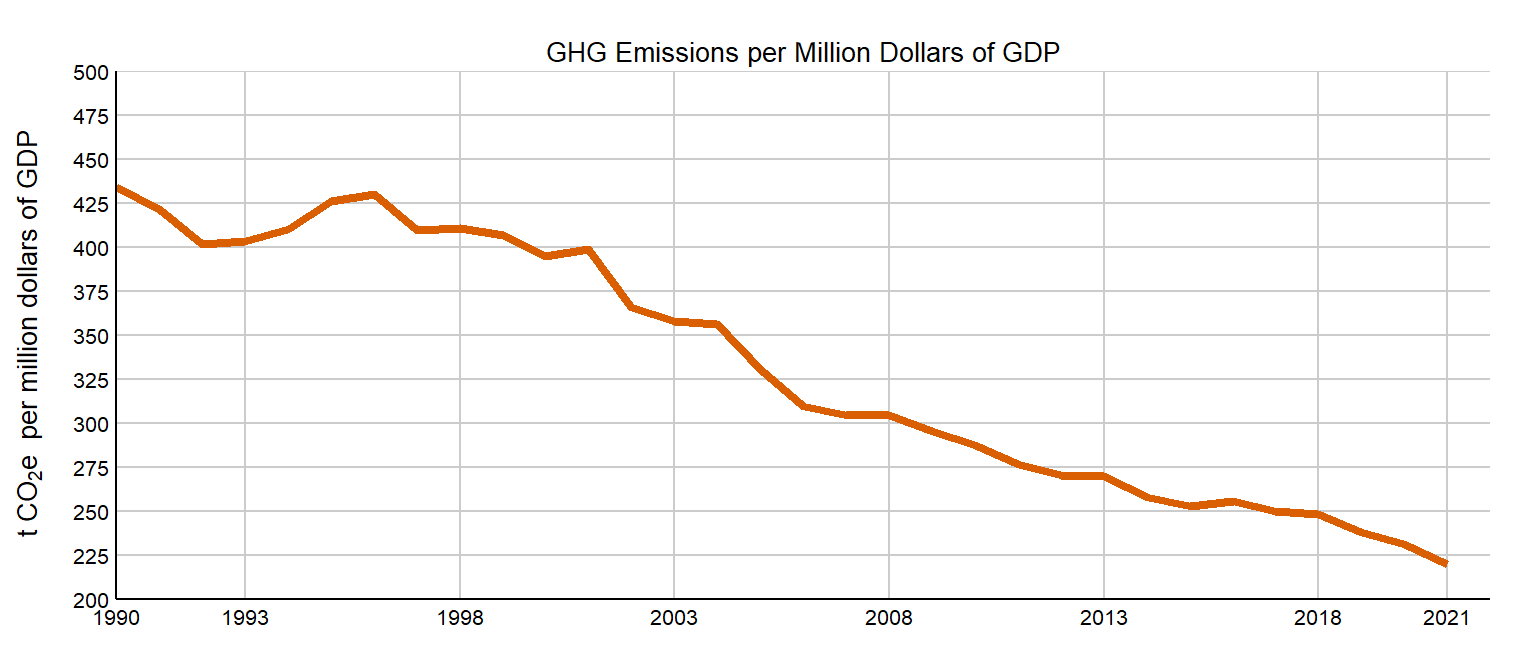



Ghg Emissions Environmental Reporting




Saskatchewan S New Climate Change Strategy Reckless Endangerment Darrin Qualman




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




Global Warming




Chile Commits To 30 Percent Reduction Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By 30 Nrdc



1



Eco Economy Indicators Carbon Emissions Epi
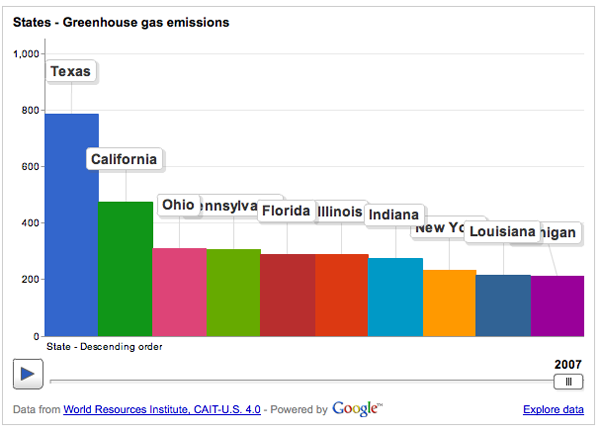



Greenhouse Gas Emissions By State Wri And Google Team Up Graphic Sociology




Dhbbvyyn33 Tum




File Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector 1990 05 In Carbon Dioxide Equivalents Epa 10 Png Wikimedia Commons
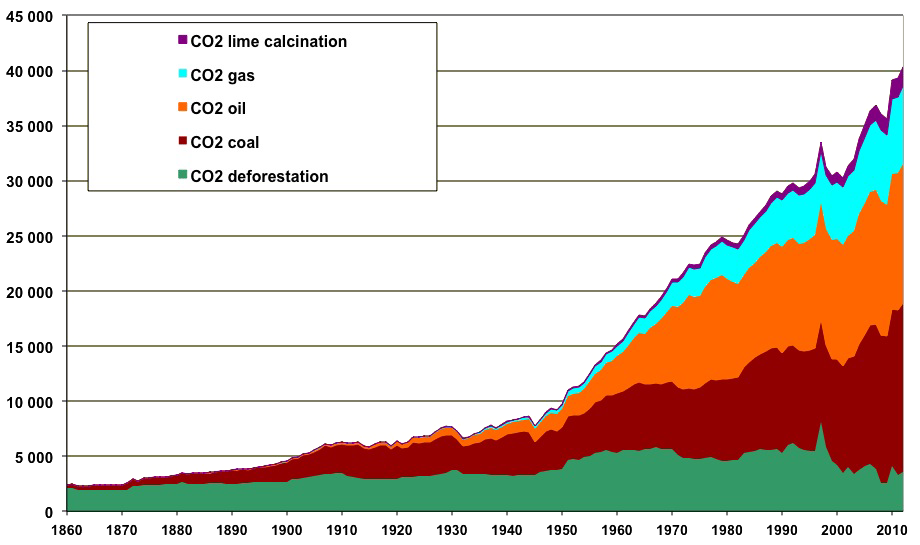



How Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Presently Evolve Jean Marc Jancovici




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By China Wikipedia
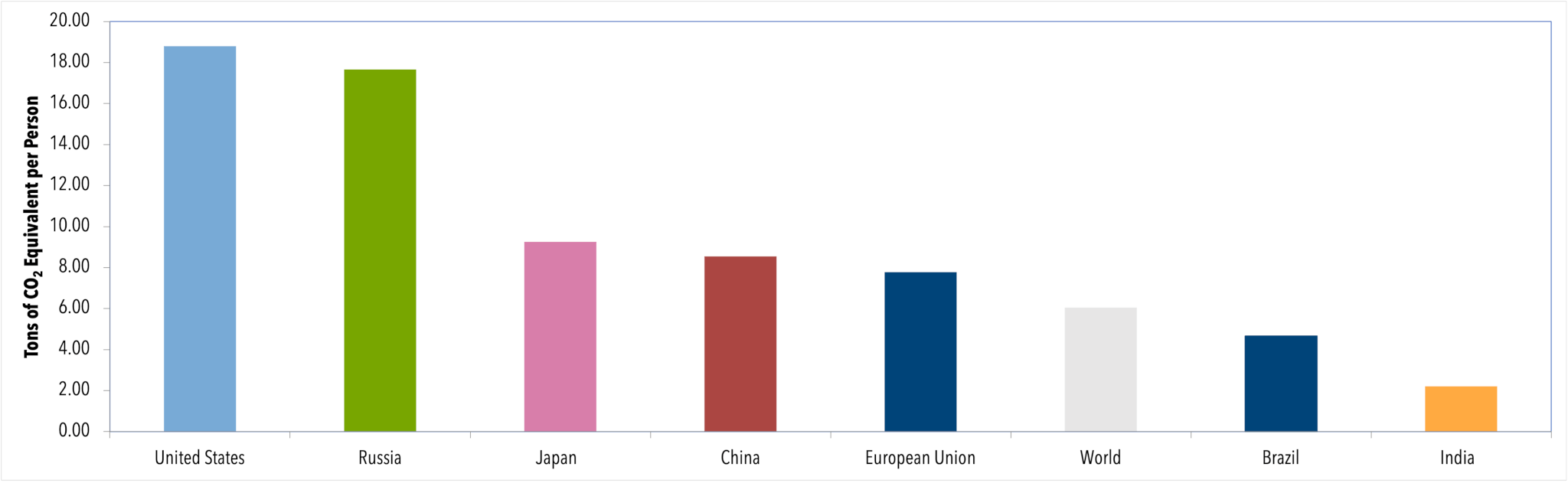



Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions



Chart How Ambitious Is The Uk S Emissions Target Statista




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus




Bill Ripple Graph Greenhouse Gas Emissions 2 Perfect Formula Diet Perfect Formula Diet
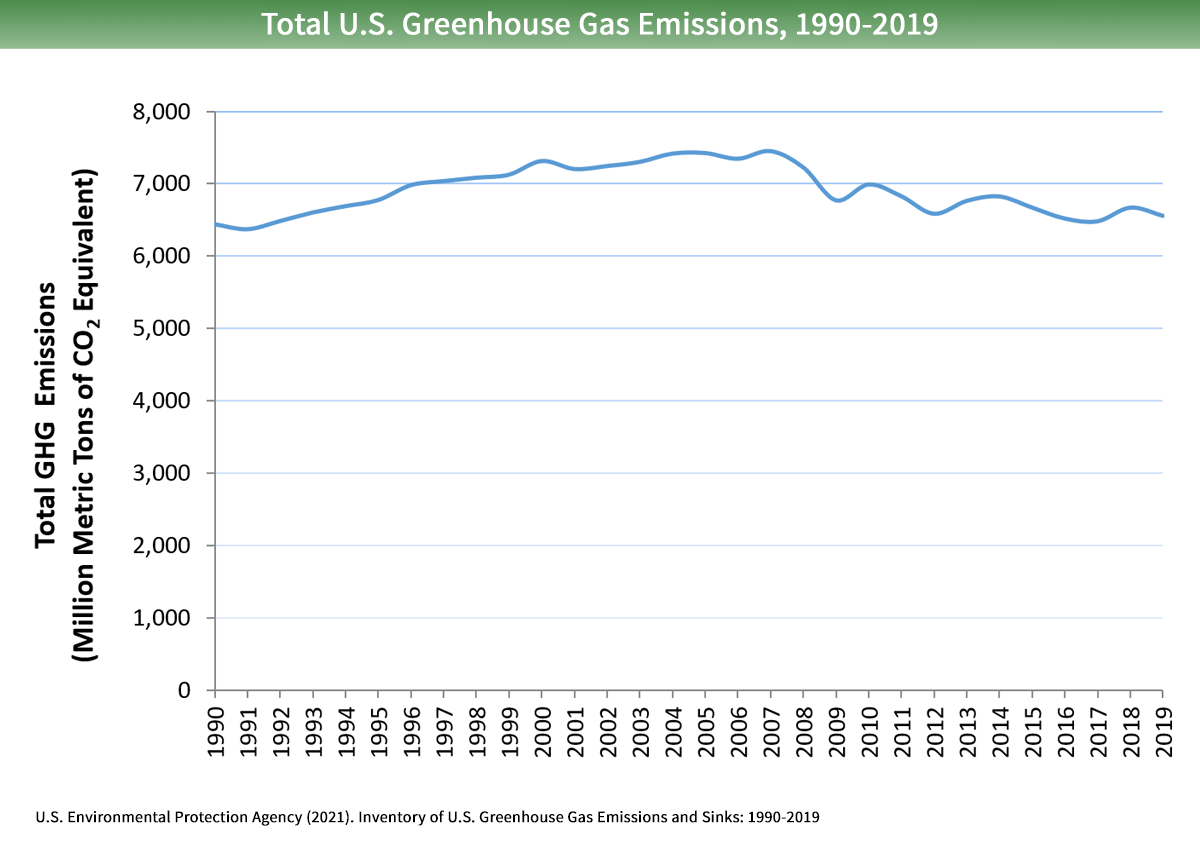



Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa
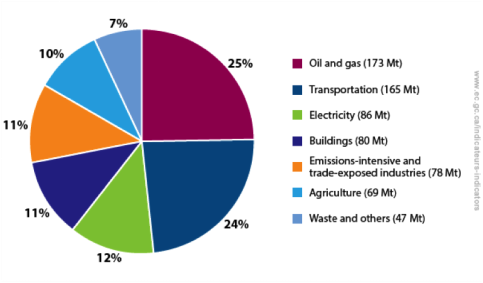



Effects Greenhouse Effect




Jsavill Angustaylormp Show Us Your Lnp Greenhouse Gas Emissions Graph We Can See The Erf Is Working Not Climatechange Auspol Myjslnpfile T Co 0aeungzvuw



c News Special Reports Greenhouse Gas Emissions Rising
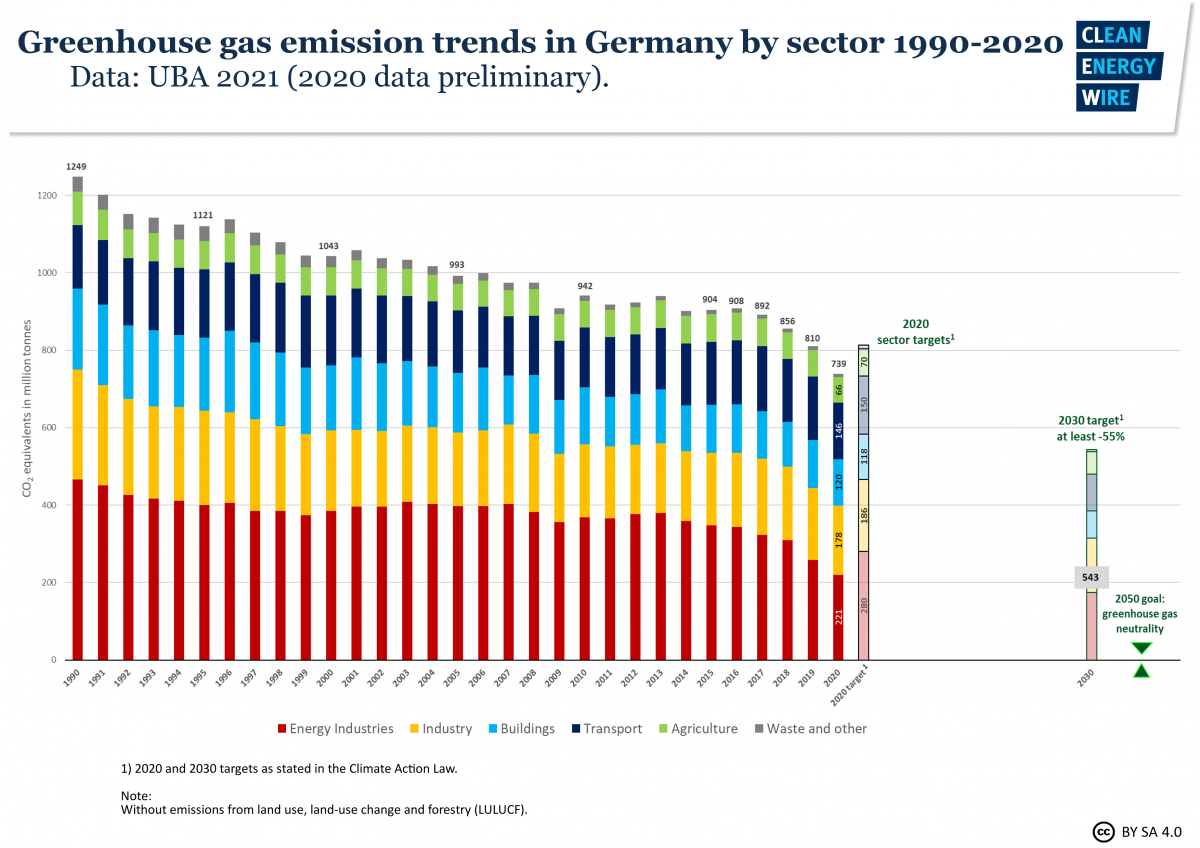



Germany Sees Record Greenhouse Gas Emission Fall Due To Pandemic Renewables Clean Energy Wire




Amazon Ghg Emissions Globally By Source 18 Statista



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming
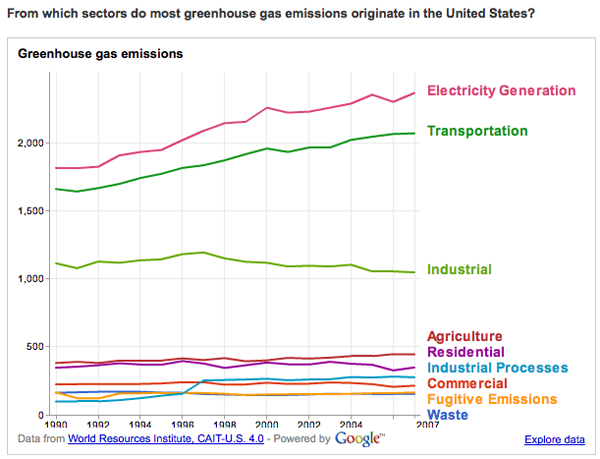



Greenhouse Gas Emissions By State Wri And Google Team Up Graphic Sociology
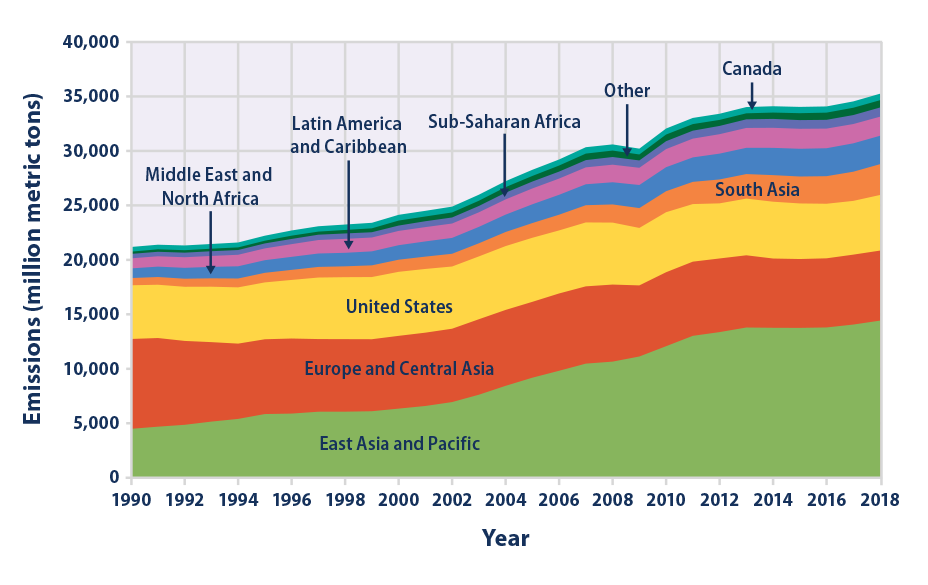



W Edyfjigr0fxm




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By The United Kingdom Wikipedia
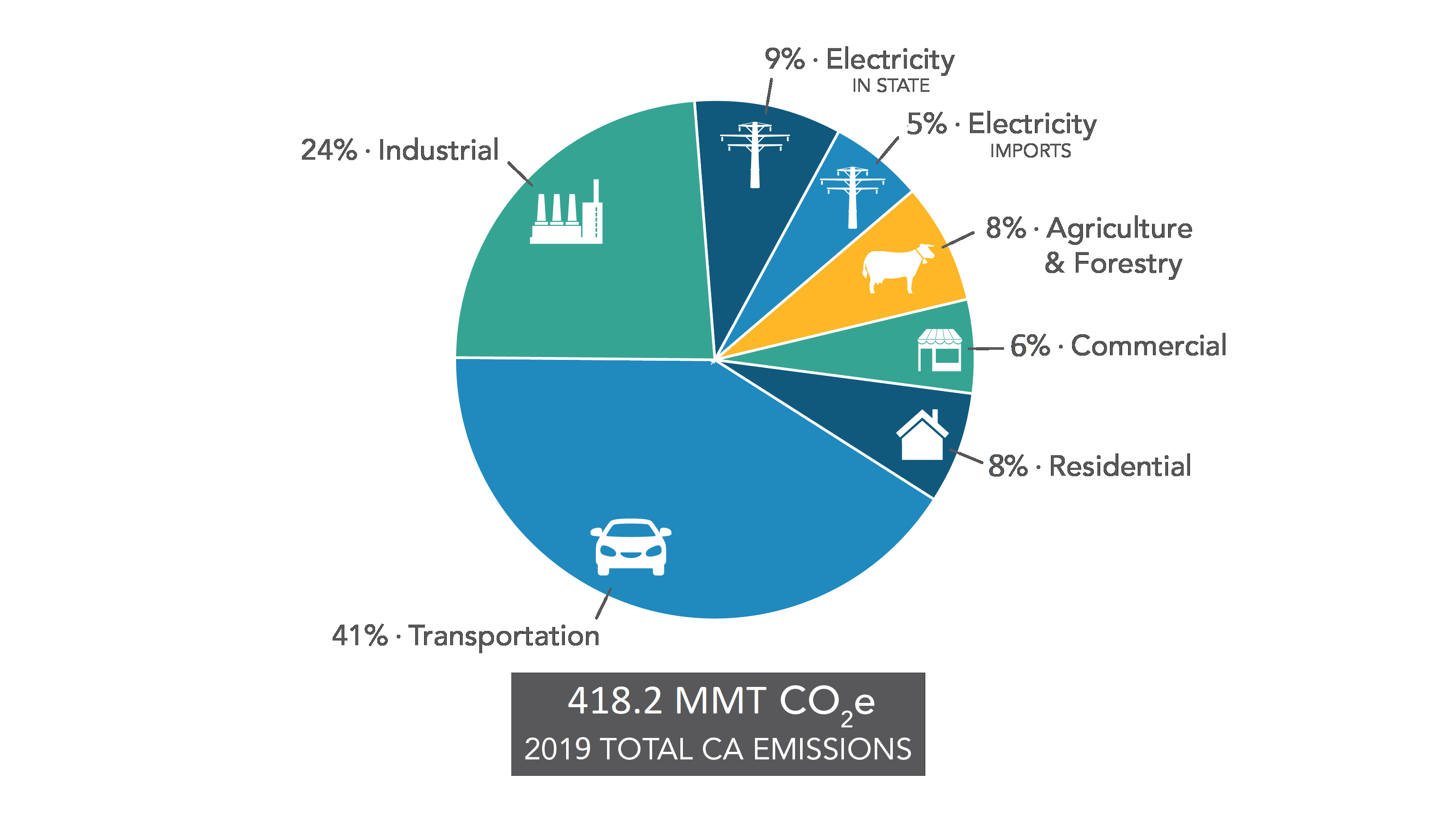



Ghg Emission Inventory Graphs California Air Resources Board
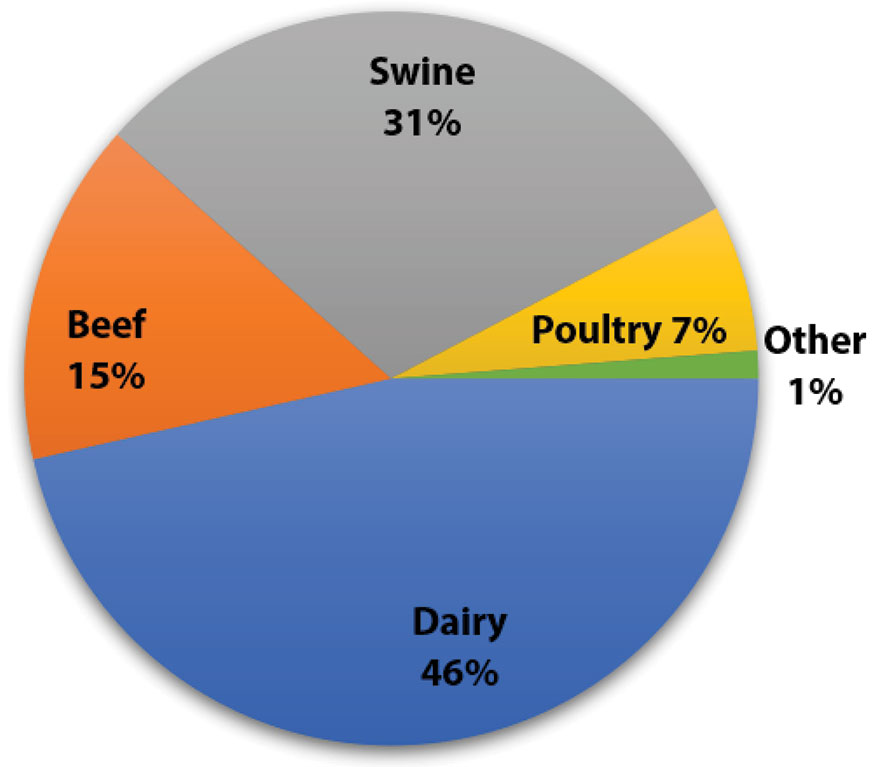



Agriculture And Greenhouse Gas Emissions G310 Mu Extension




California Plans To Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions 40 By 30 Today In Energy U S Energy Information Administration Eia




More Than Half Of All Co2 Emissions Since 1751 Emitted In The Last 30 Years




Analysis Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions In The European Union Member States With The Use Of An Agglomeration Algorithm Sciencedirect
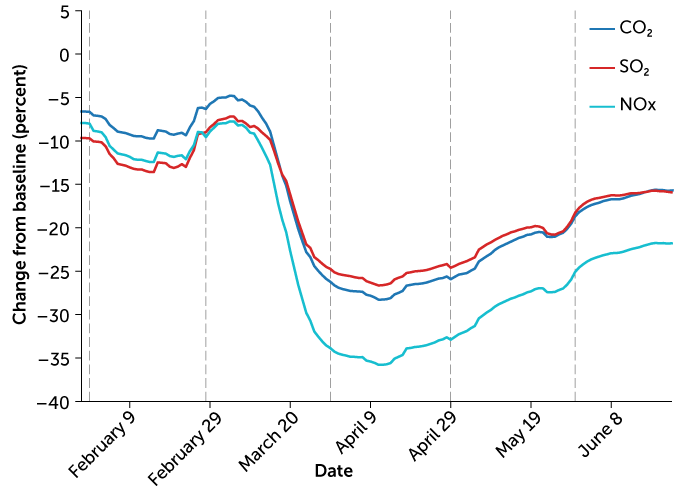



Covid 19 S Emissions Reductions Won T Impact Climate Change Science News




Graph Of The Day Noaa Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Aggi 1700 15 Desdemona Despair



Total Greenhouse Gas Emission Trends And Projections In Europe European Environment Agency




Net Zero What Internationale Politik Quarterly




Global Emissions Climate Change Us Epa Global Warming Climate Change Global




Worthwhile Canadian Initiative We Can T Get To Kyoto From Here And There S No Point In Pretending That We Can




Double Bar Graphs Real World Statistics Ck 12 Foundation
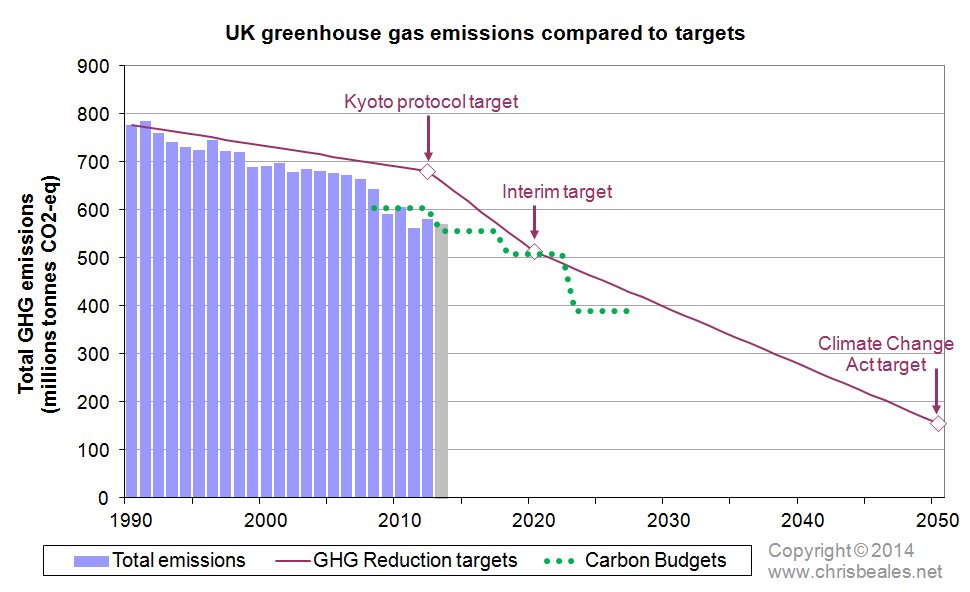



Emissions Targets Current Uk Targets
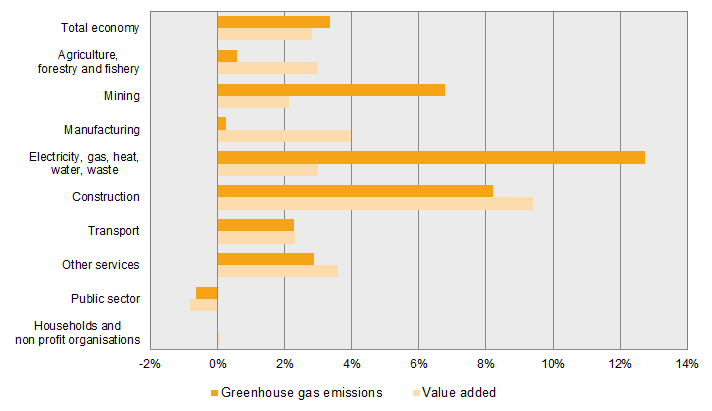



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Increased In First Quarter Of 18



Chart China Beats U S Europe In Combined Greenhouse Gases Statista




Nasa Giss Nasa News Feature Releases Greenhouse Emissions Growth Slowed Over Past Decade




Energy And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Ghgs




Greenhouse Gases Archives Darrin Qualman




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Are Set To Rise Fast In 21 The Economist



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿